Clarity for DSE Investors.
Track. Analyze. Act.
Real-time P&L, smart alerts, and deep analysis — everything DSE investors need for sharper decisions.
Built for the Dhaka Stock Exchange
app.fintrail.net
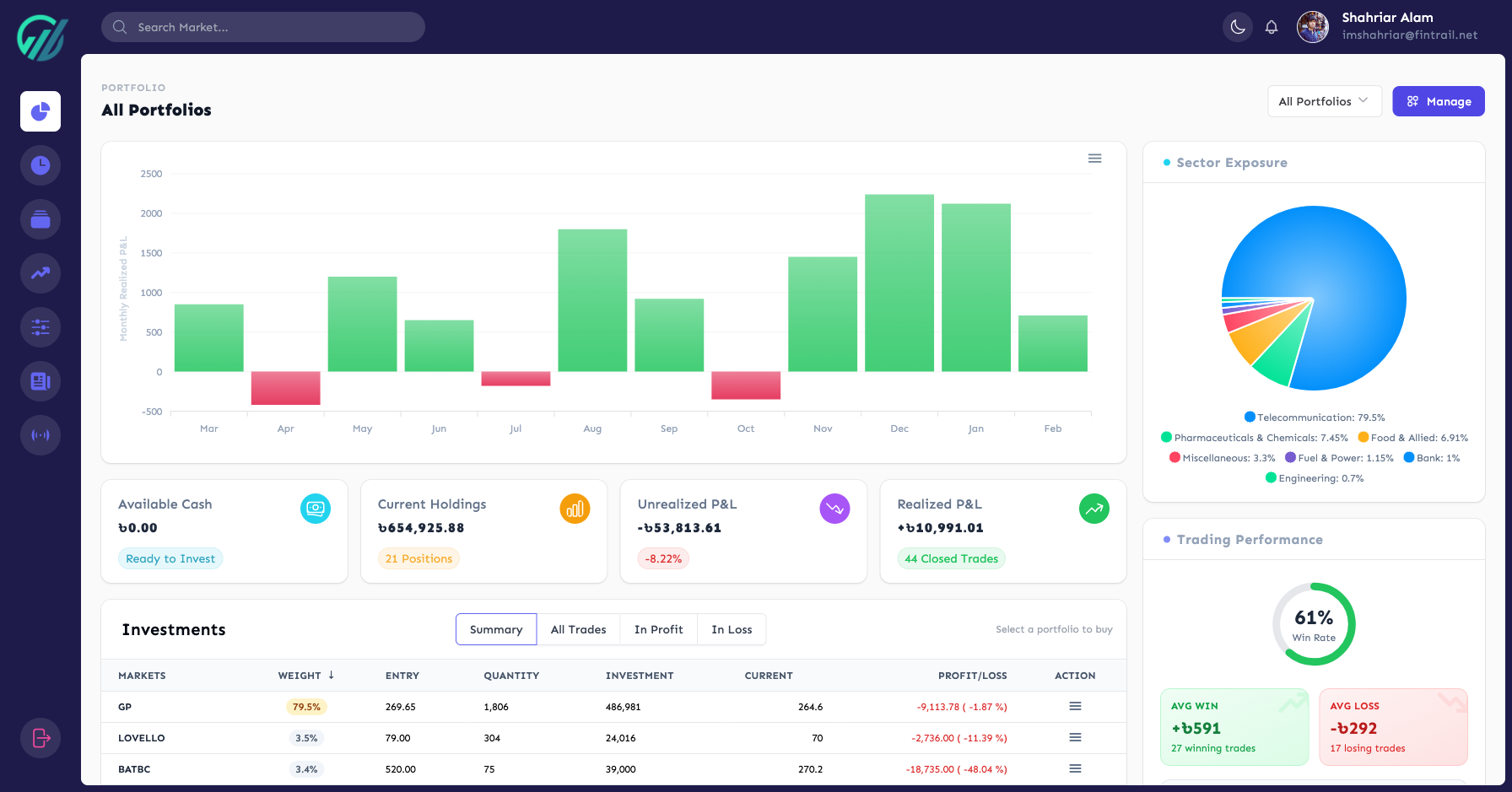
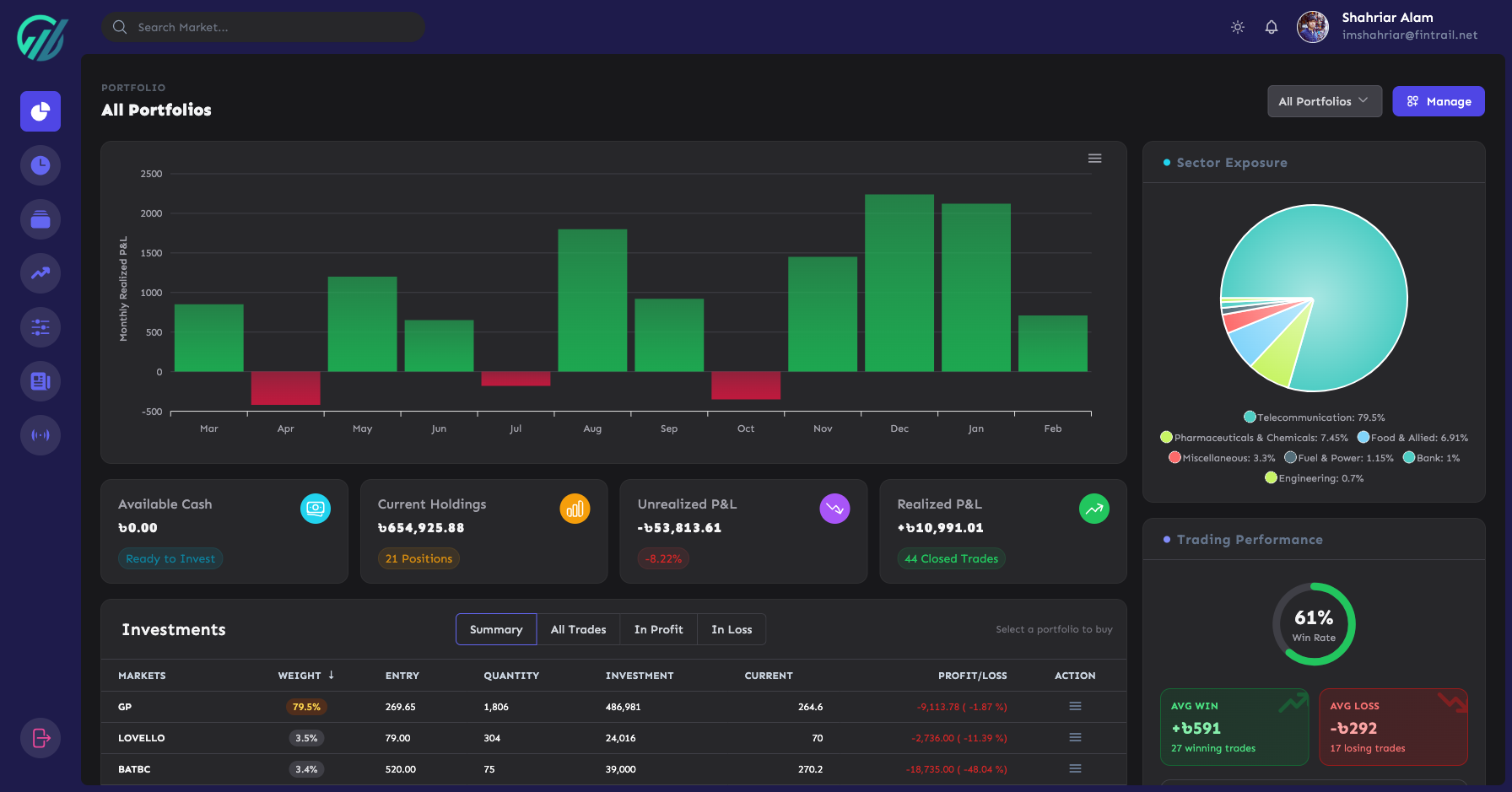
Portfolio P&L Live valuation, gains, and allocation across every holding.
60+ screener filters Fundamentals, technicals, and sector — in seconds.
Live market pulse Indices, movers, sector heatmap, and sentiment — real time.


